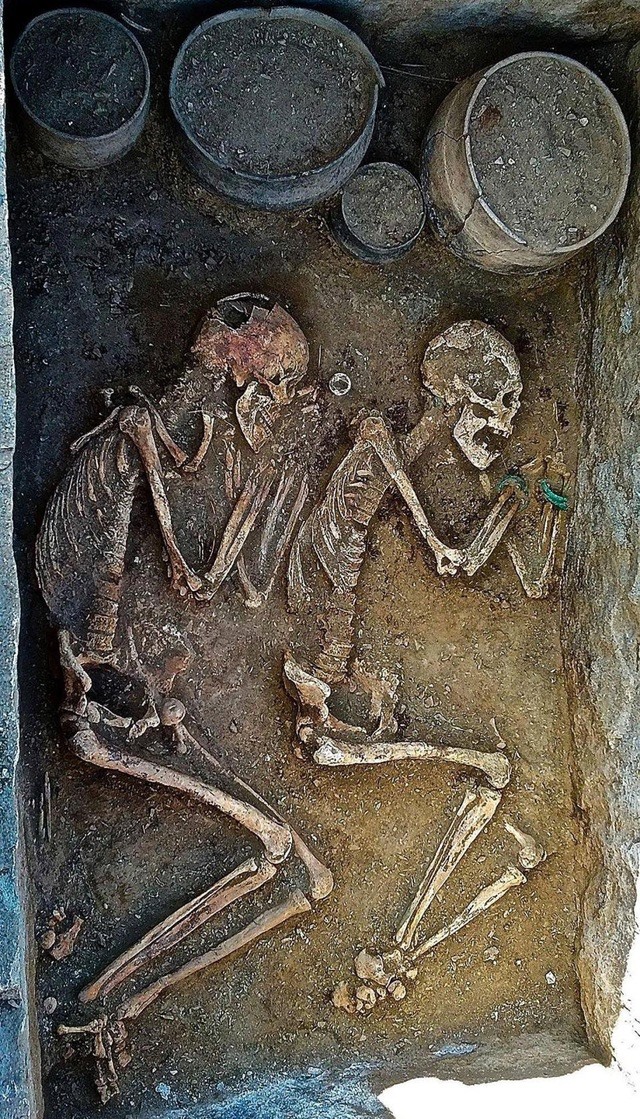
Chinese archaeologists have published research on the tomb of a couple embracing each other dating back to the Northern Wei Dynasty (386-534) more than 1,600 years ago.
Ancient city wall in Datong city, Shanxi province, northern China, where a 1,600-year-old lover’s tomb was discovered. Photo: Xinhua/CFP
Xinhua News Agency quoted information from Jilin University as saying that the ancient tomb was first excavated in Datong city, Shanxi province, northern China, in 2020.
The couple lies together in a coffin buried in the same grave. The man wrapped his arms around his lover’s waist, and the woman nestled into his chest, resting her head on her lover’s shoulder. Researchers also found a silver ring on the ring finger of the woman’s left hand.
Further analysis of the skeleton revealed an unhealed fracture on the man’s right arm, while the woman’s skeleton appeared healthy. This discovery suggests that the two may have committed suicide.
According to the research team, although several tombs of lovers from the Northern Wei period have been discovered in China , new archaeological discoveries of well-preserved tombs in Shanxi province are quite rare.
Researchers say such tombs help better explain social perceptions of human life and death, as well as of love at that time, when the coexistence of many ethnic groups promoted promote the rise and spread of pluralistic characteristics.
The ancient Datong region was once a major intersection of ethnic cultures, where the desire for love flourished at that time. The ring on the finger of the female tomb owner was mainly used to signify love or marriage rather than as mere jewelry during the Northern Wei Dynasty in northern China.
Lovers’ tombs have more than 6,000 years of history around the world, including the tomb of Lover Valdaro found in Italy and the pair of remains “embracing each other” for 6,000 years in Alepotrypa cave, Peloponnese, southern Greece .
 Valdaro’s Lover’s Tomb. Photo: Wiki
Valdaro’s Lover’s Tomb. Photo: Wiki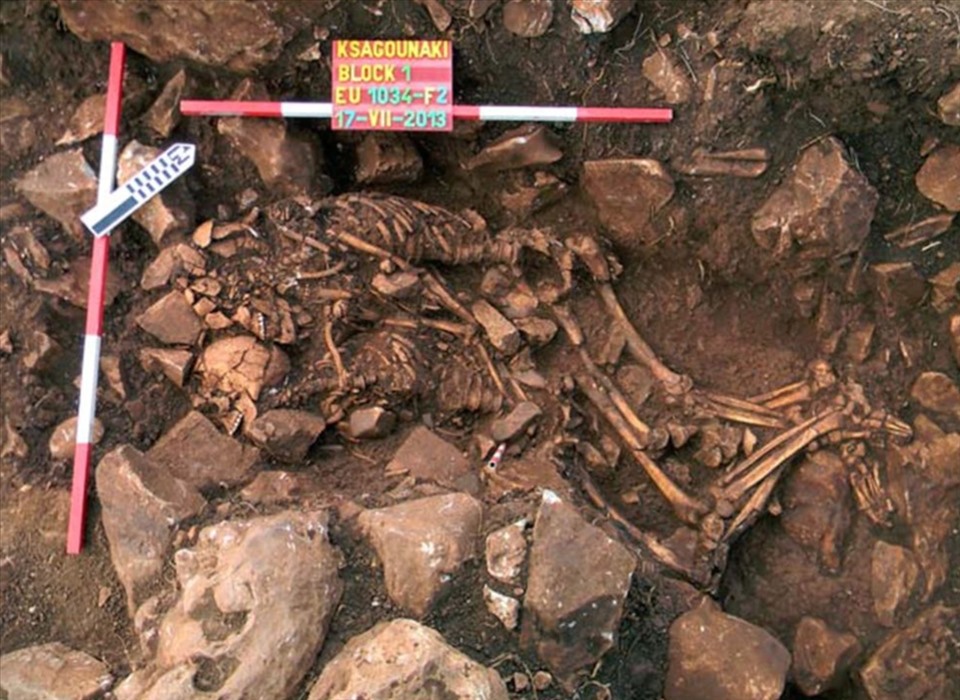 The pair of remains “embraced each other inseparably” for 6,000 years in Greece. Photo: Greek Ministry of Culture, Education and Religion
The pair of remains “embraced each other inseparably” for 6,000 years in Greece. Photo: Greek Ministry of Culture, Education and Religion
Domestic and foreign researchers, including researchers from the Datong Institute of Archaeology, Jilin University and Xiamen University, have conducted joint studies on the tomb excavated in Shanxi . An article about this research was published in the International Journal of Osteoarcheology.





