In 1900, the British Museum exhibit known as the Gebelein Man was acquired along by Sir Wallis Budge, then keeper of the British Museum’s Egyptian Department. All six bodies were excavated under Budge’s oversight in 1896 from separate shallow sand graves in the ancient Egyptian desert town of Gebelein, about 25 miles (40 kilometers) south of Thebes.
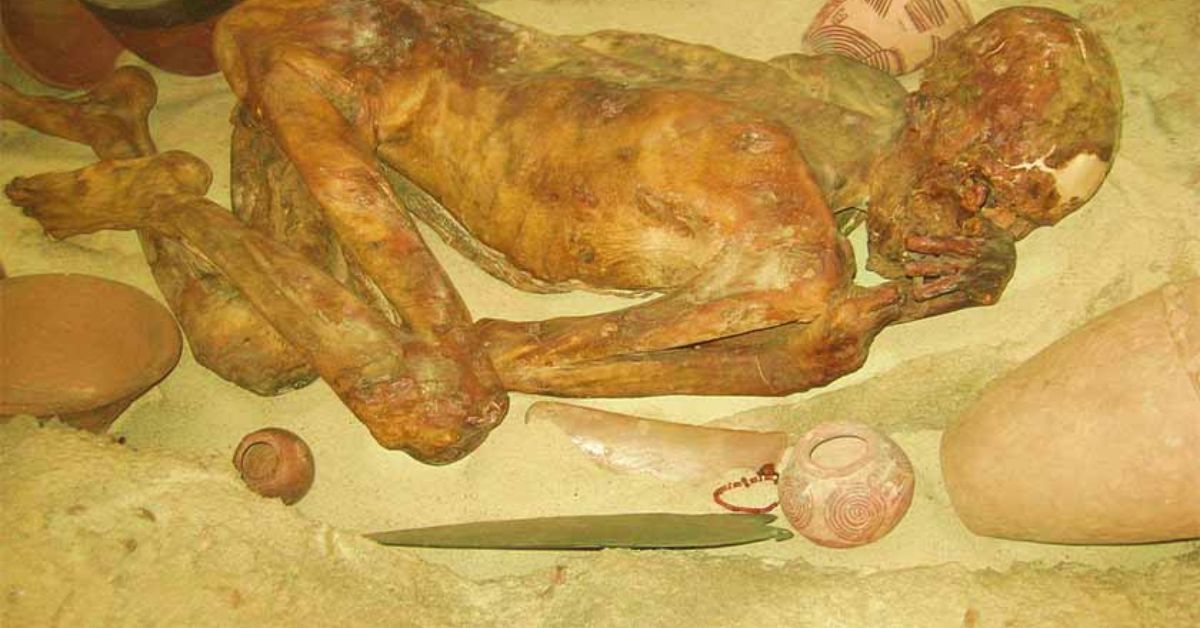
Gebelein Man Is a Predynastic Natural Dried-in-the-sun Mummy
While ancient Egypt is famous for its mummification practices, what is special about the six Gebelein mummies is that they are natural mummies from around 3400 BC, the Late Predynastic period.
Artificial preservation of the dead was only widely practiced in Egypt from around 2600-2100 BC, during the Late Old Kingdom period. However, there is now some evidence that resins and linen wrappings were used to preserve the bodies of the dead as early as 3500 BC.
The Egyptian natural mummy technique involved drying the dead body in the hot sun on a sand base until completely free of moisture. Direct contact with the hot dry sand naturally dried and preserved the bodies of Gebelein Man.
Two of the Gebelein mummies were identified as males and one as a female, while the sex of the other three was not possible to determine.
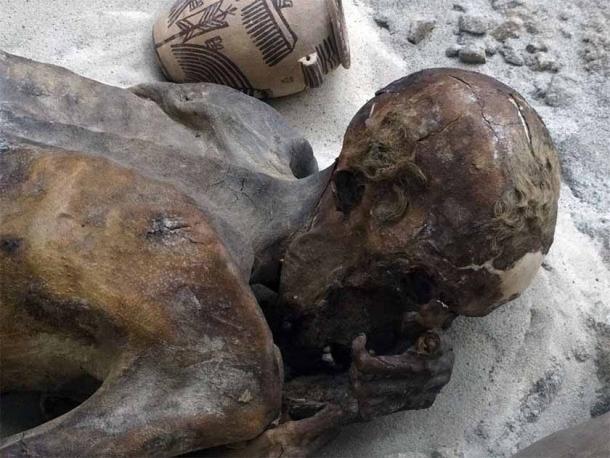

The head of Gebelein Man showing the preserved hair from a photo taken in 2011. (Fæ / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Gebelein, erstwhile “Ginger”, Man
Of the six Gebelein mummies, only the first one excavated, has been continuously exhibited, except for maintenance, since 1901. Although there was another male mummy in the Gebelein group, it is specimen EA 32751 who is widely known as Gebelein Man. He was originally nicknamed Ginger owing to the tufts of red hair still on his skull but recent policies governing ethical treatment of human remains have caused the nickname to be dropped.
Gebelein Man was wrapped in matting and buried in a contracted, almost fetal position that was usual of burials in Egypt until the mature Late Kingdom period, when bodies began to be buried fully extended. Religious reasons perhaps accounted for the change, but it is possible also that the development of artificial mummification dictated it, as an extended position made mummification easier.
Gebelein Man is exhibited in a case in which the stone-lined sand grave from which he was exhumed has been reconstructed. The display includes clay pots and bowls and other grave goods typical of Predynastic burials. However, these do not belong to the graves of any of the Gebelein mummies but are instead from similar graves of the period. This is because, although Budge did record the recovery of pots and flints, his acquisition did not extend to these items.
Gebelein Man was the first Predynastic mummy to go on display in the British Museum’s first Egyptian Room. In fact, the only other Gebelein mummy to be exhibited to the public occasionally is the lone female in the group.
So remarkably well-preserved was Gebelein Man’s corpse that not only were his facial features and hair still visible, a wound on the surface of his skin under his left shoulder blade could also still be seen. But it was more than a hundred years later that its sinister significance was understood.
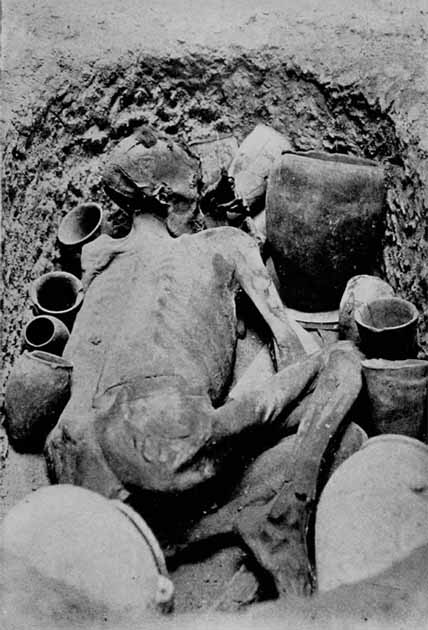

Plate from By Nile and Tigris volume 2, published in 1920 showing how the body of Gebelein Man was displayed in the British Museum at that time. (British Museum / Public domain)
Death by Murder Most Foul
Twenty-first-century advances in forensic technology brought the next big breakthrough in understanding how Gebelein Man lived … and died. To carry out the examination, in 2012, Gebelein Man, who’s rarely been moved since first going on display in 1901, was carried carefully on a duvet and taken by van to the nearby to Bupa Cromwell Hospital. Here, he was subjected to high-resolution scans, just 30 seconds of scans giving enough data for a detailed look at his insides. The data was then examined using a virtual autopsy table. The technology, from Sweden, allows virtual rotation, enlargement, and cross-sectioning of skin.
Dr Daniel Antoine, the museum’s curator for physical anthropology, told the BBC in 2012: “There’s a wound on the surface of his skin, which people have been able to see for the last 100 years, but it’s only through looking inside his body we’ve seen than his shoulder blade is damaged and the rib under the shoulder blade is also damaged. All of this suggests a violent death.” He died by murder, in short.
The scans of Gebelein Man’s skeleton revealed he was a young, muscular man aged between 18 and 21 years at the time of death. The scan of his shoulder wound showed that it was a penetrating wound that had gone through his left shoulder blade and ribs to puncture the left lung. The wound was thought to be a fatal one as it was severe and there was no sign of healing around the muscle and bone.
The skeleton bore no defensive injuries, leading investigators to conclude that he was taken by surprise and died a quick death. Thus, he was probably killed by a murderous stab to his back during peacetime.
The murder weapon would have been a pointed instrument that was either a projectile point or a dagger. A copper or silver dagger was most likely. And copper and silver blades 6-6.5 inches (15-16.5 centimeters) long and 1.5-2 inches (4-5 centimeters) wide were common in Egypt at the time of his murder. Almost the entire length of such a blade was pushed into his back in the attack that caused his death.
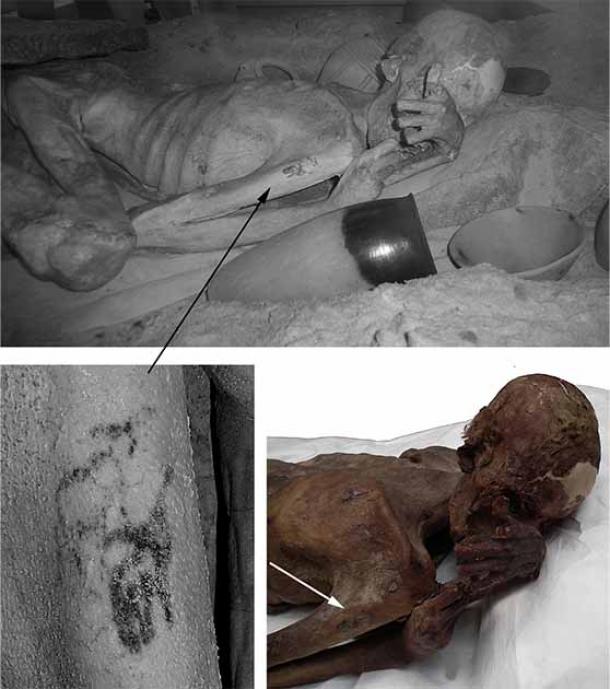
Top: Infrared image of the male mummy known as Gebelein Man. Lower left: Detail of the tattoos observed on his right arm under infrared light. Lower right: The mummy and tattoos under normal lighting conditions. (British Museum blog)
Gebelein Man’s Figural Tattoos: Oldest in Africa!
But that is not the end of the story. Gebelein Man had other surprises in store for researchers. When the bodies of Gebelein Man and Woman were re-examined as part of a conservation program in 2018, another extraordinary discovery was made. Faint smudges on their arms, hitherto thought to be unimportant, were revealed under infrared scans to be tattoos. This pushed back earliest evidence of the practice in Africa by a thousand years.
The man’s tattoos, moreover, were figural, representing two slightly overlapping horned animals, thought to be a wild bull with a long tail and impressive horns and a Barbary sheep with curving horns and humped shoulders. The woman’s tattoos were more abstract and difficult to interpret.
Hitherto, the only evidence for tattooing from the Predynastic Egypt came from abstract tattoos etched on female figurines, leading archaeologists to believe that tattooing of women was practiced as part of fertility rites in this periodBut Gebelein Man has completely rewritten the earliest evidence of the practice to include males and figural tattoos as well. The motifs tattooed on his upper arm led researchers to believe that Predynastic Egyptian men may have sported tattoos as symbols of virility and strength.
For more than 125 years, Gebelein Man’s remains have provided fascinating insights into Predynastic Egypt. And now, thanks to modern science, we know that Gebelein Man was attacked from behind by an unknown murderer nearly 5,400 years ago!





