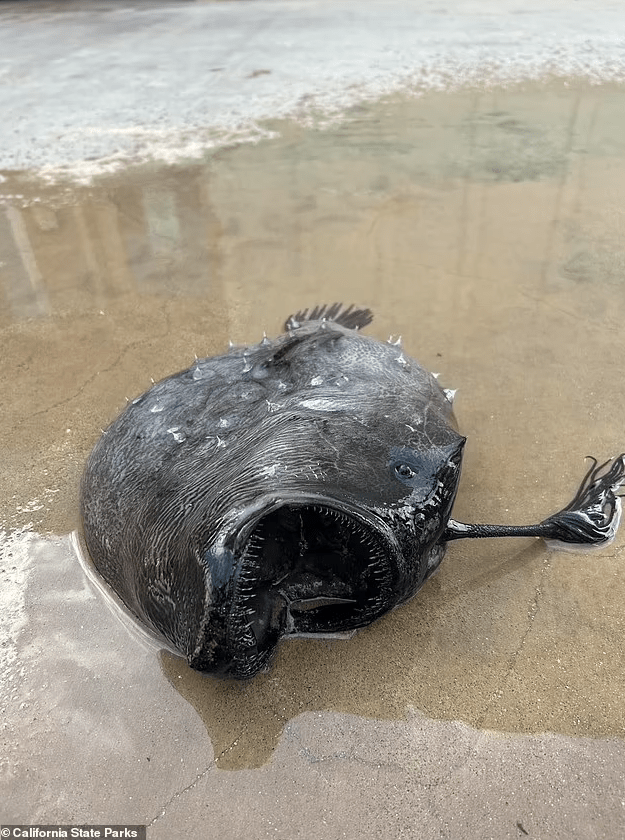
A bizarre and rare deep-sea creature, the Pacific Football Fish, caused quite a sensation when it washed up on a California beach at Crystal Cove State Park in Newport Beach on October 13. This jet-black fish, typically found 3,000 feet below the ocean’s surface, belongs to the anglerfish family, which comprises more than 200 species of bony fish. The Pacific Football Fish stands out with its eerie appearance, characterized by completely black eyes situated on the sides of its flat head.
What makes anglerfish, including the Pacific Football Fish, unique is a dangling bioluminescent appendage protruding from their faces, which they employ to lure and capture prey in the deep, dark ocean.
]This bioluminescent lure, powered by symbiotic bacteria, acts as a fishing pole to entice prey close enough for the fish to strike with its razor-sharp teeth. However, it’s essential to note that this distinctive appendage is exclusive to females.
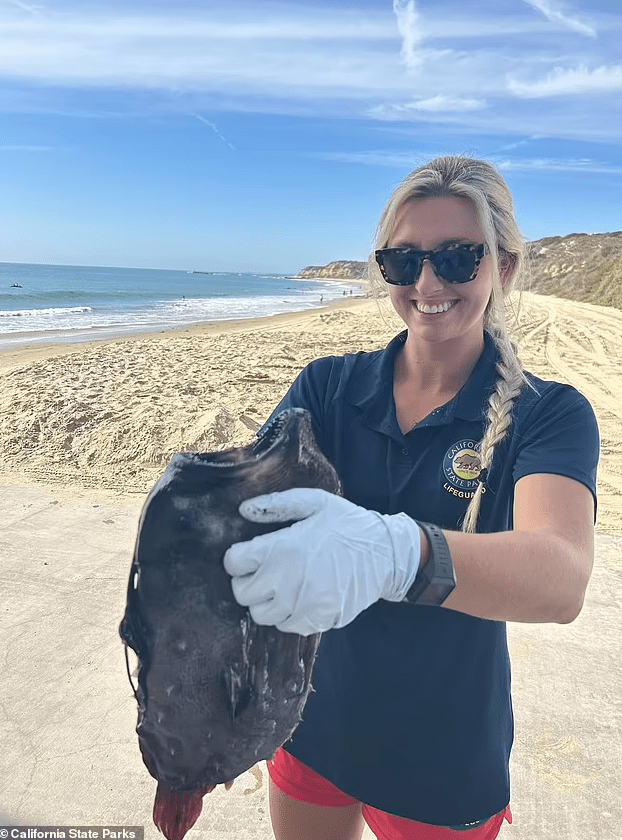

The discovery of a female Pacific Football Fish above the water’s surface is exceptionally rare, as predators usually consume them before they reach shallower waters. These female fish are identifiable by a long stalk on their heads, featuring bioluminescent tips that attract prey in the ocean’s depths. The discovery brought attention to the intriguing phenomenon of sexual dimorphism within anglerfish species, where males and females exhibit marked differences in physical characteristics.
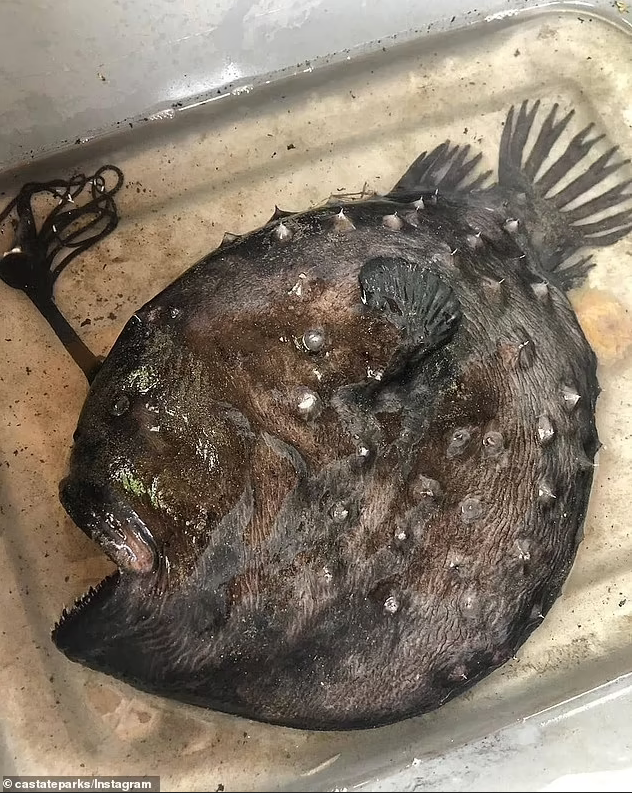

While park officials were somewhat tight-lipped about specific details regarding the creature, they did mention that female Pacific Football Fish can grow up to 24 inches in length. The find highlighted the captivating and diverse marine life concealed beneath the ocean’s surface within California’s Marine Protected Areas (MPAs). Officials emphasized the importance of continued scientific exploration and discovery in understanding these enigmatic deep-sea creatures.
‘Seeing this strange and fascinating fish is a testament to the curious diversity of marine life lurking below the water’s surface in California’s Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) and as scientists continue to learn more about these deep sea creatures, it’s important to reflect on how much is still to be learned from our wonderful and mysterious ocean,’ Crystal Cove State Park officials shared in a Facebook post.
This was a particularly significant discovery because it had been two years since the last Pacific Football Fish was found on the beach. In May 2021, a beachgoer and fisherman named Ben Estes stumbled upon another specimen, measuring 18 inches, frozen in the sand.

In 2018, scientists achieved a remarkable milestone by capturing footage of live anglerfish mating for the first time. Prior to this breakthrough, mating behavior among anglerfish was only observed in dead specimens caught in nets. The footage revealed the female’s glowing filaments extending around her body as a small male clung to her. This phenomenon was documented at a depth of 2,600 feet off Portugal’s São Jorge Island by deep-sea explorers Kirsten and Joachim Jakobsen, who used a remotely operated vehicle.
The unique, permanent attachment of males to females in anglerfish represents a form of “anatomical joining” not found in humans, except for extremely rare cases of genetically identical twins. This discovery underscores the enigmatic and captivating nature of deep-sea life, shedding light on the fascinating and peculiar creatures inhabiting the depths of Earth’s oceans.