The aboriginal people of the Paiute tribe in Nevada (USA) have legends about their ancestors and red-haired giants called Si-Te-Cah. Although only a small group, Si-Te-Cah always attacked and kidnapped Paiute tribesmen to eat.
According to legend, the Paiute fought the giants to the end and chased them to their lair. Determined to exterminate the Si-Te-Cah, the Paiute piled trees at the mouth of Lovelock cave and set fire to them. A few people who escaped from the cave were killed by arrows, and the rest in the cave also lost their lives because of the fire and smoke. Finally, an earthquake buried Lovelock Cave, erasing all traces of the red-haired giants.
Lovelock Cave in Nevada (USA) was first discovered in 1913. In 1924, an archaeological expedition from Berkeley University began to investigate and explore. Lovelock Cave – about 12 meters deep and 18 meters wide – was originally called Horseshoe Cave due to its U-shaped interior.
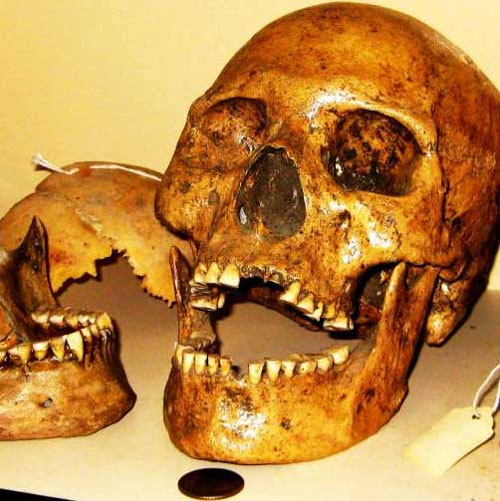 Giant skull next to normal human skull at Humboldt Museum.
Giant skull next to normal human skull at Humboldt Museum.
Many Native American tribes still pass down legends about red-haired giants and how their ancestors fought terrible wars against cannibals.
Even the Aztecs (mainly living in Central and Southern Mexico during the 14th and 15th centuries) and the Maya (the people who developed the ultimate civilization lived from the 4th to the 8th centuries in Central America and the Southern region). Southern Mexico) also confronted the northern giant race. In addition, giant vestiges are also found on all continents.
In 1931, two very large skeletons were found at the bottom of Humboldt Lake near Lovelock. A 2.5 meter tall skeleton, described as being wrapped in a plastic-covered cloth, not unlike Egyptian mummies. The remaining skeleton is 3 meters high.
In 1950, fossils of a giant with a thigh bone up to 1.2 meters long were found near Turkey’s Euphrates River and scientists thought this person was about 5 meters tall. In 1970, the skeleton of a red-haired giant was revealed in the Amazon region.
In 1976, archaeologists at the Smithsonian Museum (USA) continued to discover bones of a man about 2.5 to 3 meters tall in the Kurdish region of southern Turkey.
 A fake duck head used as a mallard decoy found inLovelock Cave is on display at the Smithsonian Museum.
A fake duck head used as a mallard decoy found inLovelock Cave is on display at the Smithsonian Museum.
In 2004, the remaining bones of a giant about 3 meters tall were discovered after a tsunami on Thailand’s Phi Phi Island. In 2005, two giant ancient tombs over 10 meters long were discovered in Syria.
The Paiute Indians called the red-haired giant Si-Te-Cah, meaning “wick-eaters” , for two reasons: wick is a plant that grows in swamps and is used by giants to build rafts to escape. ; and secondly, these people often kidnapped women who cut down wicker trees on the shores of Humboldt Lake.
Archaeologists found inside Lovelock Cave more than 10,000 artifacts and mummies of two red-haired giants – a female about 1.9 meters tall and a male more than 2.4 meters tall. Many of the artifacts from Lovelock Cave were later transferred to the Nevada Historical Society in Reno, but others also fell into the hands of private antiquities collectors.
 The trail leads to Lovelock Cave.
The trail leads to Lovelock Cave.
Today, visitors to the Humboldt Museum of Natural History in Winnemucca, Nevada (USA), will see several artifacts, skulls and jawbones of giants.
In addition, other major museums across the United States also display relics of red-haired giants – for example, the fake duck head found in Lovelock Cave is on display at the Smithsonian Museum. , bones at the Nevada State Museum.





